By PatientPoint Launch
•
25 May, 2023
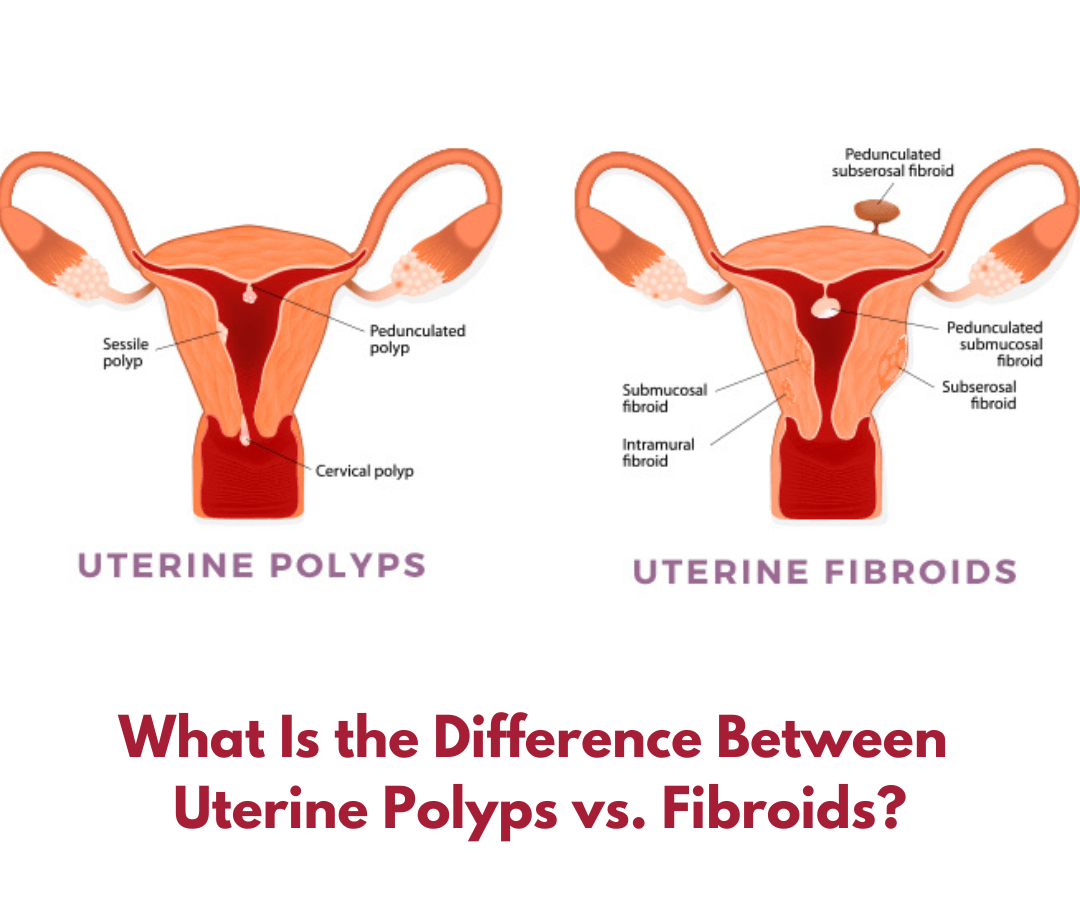
Both uterine polyps and fibroids are uterine growths and can be tricky. Due to their asymptomatic nature, they are hardly noticed, and it isn’t until one faces issues with the menstrual cycle or hardship in getting pregnant that either of the ones gets diagnosed. But what is the fundamental difference between fibroids and polyps? Polyps are the endometrial (inner lining of the uterus) outgrowths, while fibroids are the dense connective fibrous tissue arising from the smooth muscle of the uterus. Although both can cause irregular periods, heavy periods, or fertility issues, uterine fibroids do not cause cancer risk. At the same time, polyps may become more dangerous, as they can turn out to be cancerous if not treated at the correct time. Knowing the difference between polyps and fibroids prevents future problems related to health. Read on to find out more about the difference between fibroids and polyps, their symptoms, diagnosis, complications, and treatments. What Are Uterine Fibroids? Fibroids are benign tumors that arise from the uterus muscle within the uterine wall extending into the uterine cavity. People get stressed out when diagnosed with fibroids, but they need not worry, as fibroids are a non-cancerous outgrowth. Although the causes of uterine fibroids are not known, they can grow in response to the hormone called estrogen. It continues to grow throughout the reproductive years of a woman with the average circulation of estrogen levels. It is estimated that one in every five women of childbearing age may have uterine fibroids. They are primarily seen in women aged over 30. Fibroids can be treated with surgeries or fade away without surgery. However, it may cause discomforts like excessive bleeding, fertility issues, weight gain, uterine issues, painful sex, anemia, depression, and anxiety. So, it's better to have a check-up and proceed further with the doctor's advice. Symptoms of Uterine Fibroids Heavy and prolonged menstrual bleeding Pelvic pressure and pain Infertility Multiple miscarriages Distended abdomen If a woman suspects to have either of the conditions described above, it is best to talk with a physician and seek guidance from a specialist. It can help accurately diagnose fibroids or uterine polyps and plan better treatment. What Are Uterine Polyps? Uterine polyps are usually different from fibroids. Polyps are the overgrowth of cells produced in the uterus lining that does not shed during menstruation, contrasting to its usual nature of flushing out with the blood flow. Although the polyps are considered non-cancerous, they still run a small risk of becoming malignant if not treated properly. Polyps can occur in women of any age group. However, 40-49 years is the most common range. One or several polyps might be found in the body of a woman. It is vital to be evaluated by a fertility doctor if you feel discomfort. The cause of endometrial polyps is not clearly understood, but it might be developed from the overgrowth of the endometrium or other medications. Like fibroids, this can also be caused due to the abnormal response to an increase in the estrogen level. Symptoms of Endometrial Polyps Irregularities in menstruation Inter menstrual bleeding Heavy menstruation Vaginal bleeding after menopause Infertility It is highly recommended to have a health check-up once you experience these symptoms. The more you know the reason, the better you can work towards keeping yourself healthy. As uterine fibroids and endometrial polyps have significantly similar symptoms and occur simultaneously, it's essential to have a full health check from an expert doctor who knows the difference between the two. It is because polyps can lead to serious health issues like: Cancer. Heavy vaginal bleeding. Irregular menstrual periods and instability of regular cycles cause anemia. What Is the Difference Between Endometrial Polyps and Fibroids? Polyps consist of endometrial tissues, while fibroids are made of smooth muscle tissue. Uterine growths may be formed in similar locations, but polyps and fibroids differ in many good aspects. Polyps remain relatively small and rarely grow into a more extensive form than a couple of centimeters in diameter, and they might shrink on their own. On the other hand, fibroids are pretty significant in their size, and they tend to grow into gigantic proportions and stretch the uterus. They can also shrink but do not regress. Polyps tend to grow malignant, although they don't always cause cancer but pose a risk to it. Hence it is recommended to remove the polyps to prevent further trouble. On the contrary, fibroids are non-cancerous and can get cured without surgery. Although specific non-surgical methods can be employed to remove the polyps, the best non-surgical technique can be administering the hormone balancing drugs to eliminate the problem. However, surgery is the final option to remove polyps if it doesn't get cured. If you think you may have uterine polyps or fibroids, make sure you seek professional help as soon as you can. Diagnostic Methods Several diagnosis methods can be incorporated to understand whether the symptoms in your body are caused by a polyp or a fibroid. Hence further treatment can be done by the diagnosed outgrowth. Fibroids Ultrasound - The sound waves are used to get a picture of the uterus, scan for the presence of fibroids, and measure the size of the fibroids if present. Hysteroscopy - In this method, a small telescope is inserted inside your womb through the vagina and cervix so that the doctor can get a quick scan. It is the most widely used method of fibroids diagnosis inside the womb. Laparoscopy - In laparoscopy, a small telescope, known as a laparoscope with a light source and camera at one end is inserted inside your pelvis or abdomen by making a small cut at the abdomen. It is used to scan for fibroids outside the womb or in the muscles surrounding the womb. Biopsy - A small tissue is removed for further examination while performing hysteroscopy or laparoscopy in some cases. It is called a biopsy. Endometrial Polyps Transvaginal Ultrasound - A wand-like device is placed in the vaginal area that emits sound waves and creates an image of the uterus, which helps identify a polyp as an area of thickened endometrial tissues. Endometrial Biopsy - A suction catheter may be used to collect the specimen from the uterus, and uterine polyps can be confirmed by biopsy. Hysteroscopy - Hysteroscope is a device inserted through the vagina into the uterus to examine the inside of the uterus and look for outgrowth. Treatments of Fibroids and Polyps As stated above, fibroids are more accessible to treat non surgically than polyps. Let's look at different methods used to treat polyps and fibroids. Fibroids Surgeries are not usually required to treat fibroids, and several non-surgical techniques can easily remove fibroids. Some of them are listed below: Non-surgical Methods: Hormone therapy - The estrogen levels can be lowered by using estrogen-progestin contraceptives, progesterone-containing intrauterine devices, progestin implants, pills, gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists, or gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists some hormonal injections. This helps in decreasing the stimulation of the fibroids. Tranexamic acid - This medication can be taken to ease heavy menstrual periods, and it is used on heavy bleeding days to decrease the bleeding. Embolization - Uterine artery embolization is a technique used to cut off the blood flow to the fibroids. Radiofrequency ablation - In this procedure, the uterine fibroids are destroyed by using radio-frequency energy, which helps shrink the blood vessels that feed them. Use of NSAIDs - Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are non-hormonal medications that can effectively relieve pain related to fibroids. Surgical Methods Involve: Myomectomy - The surgical removal of the fibroids from the uterine wall. Hysterectomy - Removal of the entire uterus by surgery. Endometrial Polyps Small polyps can be resolved soon without any surgery. However, if the polyps have a cancer risk, it is best to have a surgical treatment. Certain hormonal medications like progestin and gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists can lessen the symptoms of the polyps. Surgical removal by hysteroscopy can be used to remove the polyps. For a check-up of the uterus, book an appointment with Georgia Vascular Institute(GVI). Contact us to schedule an appointment or fill out the contact form.